21.6.3. Gbasf2¶
Gbasf2 is the command-line client for submitting grid-based basf2 jobs. Data and MC samples are distributed in many storage sites around the world, and the gbasf2 tools allow you to access and analyze them.
The same steering files used with basf2 work with gbasf2, and the usual workflow is:
First developing a basf2 steering file.
Testing it locally.
Locate your input files.
Submit jobs to the grid with the same steering file.
Download the output to perform the offline analysis (plots, fits, etc.)
Warning
Before getting started, make sure you understand the following:
The GRID is NOT a local computing system like KEKCC.
Once you submit jobs, they will be assigned to computing systems around the world.
If your job is problematic, it will be distributed to the world and all sites will be affected.
Go to computing getting started and verify that you have the prerequisites. You need:
A system with SL6 or CentOS 7.
A valid grid certificate issued within a year and installed in
~/.globusin.pemformat.Belle Virtual Organization (VO) membership registered or renewed within a year at the VOMS server.
Registration in DIRAC.
Note
It is required to join the comp users forum, where you can ask for help and receive announcements on releases and system issues.
Installing gbasf2¶
Since the DIRAC user interface relies on some middleware components, this limits the operating environments in which gbasf2 can function. At this moment, only SL6 and CentOS 7 are supported.
Also, unfortunately at this moment the basf2 and gbasf2 environments are not compatible. This means gbasf2 requires
a fresh ssh session (without sourcing b2setup).
Note
Be sure that the userkey.pem has the rw permissions only for the owner and no permission to the others.
You should see -rw------- with ls -l ~/.globus/userkey.pem. Otherwise, use
chmod 600 ~/.globus/userkey.pem
Open a terminal and create a directory to store your gbasf2 installation. Inside, let’s download the installation script:
mkdir gbasf2 && cd gbasf2
wget -N http://dirac.cc.kek.jp/dirac/dirac-install.py
python dirac-install.py -V Belle-KEK
Execute the installation script specifying the installation type with -V Belle-KEK:
python dirac-install.py -V Belle-KEK
Check that the execution finished without errors.
Tip
If you see error messages, a gbasf2 troubleshooting is available.
Proceed to the post-installation configuration:
source bashrc && dirac-proxy-init -x
dirac-configure defaults-Belle-KEK.cfg
Setting your gbasf2 environment¶
Once the above installation is done, you only need to execute two commands every time that you open a new terminal:
source ~/gbasf2/BelleDIRAC/gbasf2/tools/setup
gb2_proxy_init -g belle
It will ask for your certificate password before generating your credentials. Once created, your proxy will be valid
for 24 hours. You just need to execute gb2_proxy_init -g belle again if your credentials expire.
Locating datasets on the grid¶
The most common task as user of the grid is the submission of jobs with input files
From the official Belle MC campaigns.
From the official data reprocessing and skims.
Files are stored around the world in the different storage elements. Fortunately, as user you don’t have to worry about the physical location. A file catalog keeps the record of where the files are located, and you just need to provide a logical identifier of the interesting samples for your analysis.
Datasets and Datablocks¶
A logical file name (LFN) is the unique identifier of a file in the Belle II grid in the form of a unix-like file path (starting always with /belle):
/belle/data_type/some_more_directories/dataset/datablock/file
A replica catalog resolves the LFN, and provides the information of where to find the files. Then, you only need to provide the LFN(s) relevant for your analysis, without dealing with the physical location of the samples.
Files are classified inside datasets. Examples of LFNs for datasets are:
# A mdst dataset of data from exp 10
/belle/Data/proc/release-04-02-02/DB00000938/proc11/prod00013368/e0010/4S/r03774/mdst
# A MC sample of charged B mesons
/belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00009435/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/charged/mdst
By design, a directory on the grid can only contain 1000 files at most. For this reason, the concept of datablock
is introduced. Each dataset is subdivided by directories with name subXX, where the last two digits are sequential
(sub00, sub01, ...).
Key points
By design, each datablock contains a maximum of 1000 files.
If a dataset contains more than 1000 files, at least it will be subdivided in two datablocks.
The command-line tool for listing the content of a directory on the grid is gb2_ds_list
(it is equivalent to ls on your local system). You can use it to see how many datablock contains each dataset.
Tip
All the gbasf2 command-line tools (sometimes called gb2 tools) have the flags --help
and --usage to see all the available options.
Exercise
Use gb2_ds_list to see how datablocks contain the dataset
/belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00012386/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/eeee/mdst
Hint
Remember to set your gbasf2 environment first, otherwise the tool will not be found.
Solution
gb2_ds_list /belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00012386/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/eeee/mdst
will show you that the dataset contains 3 datablocks.
Note
Sometimes, in the documentation (such as Confluence pages) we refer to the logical path name (LPN) of datasets and datablocks, while for files we keep LFN. In practice, LFN and LPN are the same thing.
The Dataset Searcher¶
The Dataset Searcher is a web application to find datasets on the grid. Go to the DIRAC webportal and then open Menu (the icon at the left-bottom) -> BelleDIRACApps -> Dataset Searcher.
You have the option of searching between data or MC, samples with beam background (BGx1) or without (BGx0), and several fields to refine your search. Play with all the available options and get familiar with them.
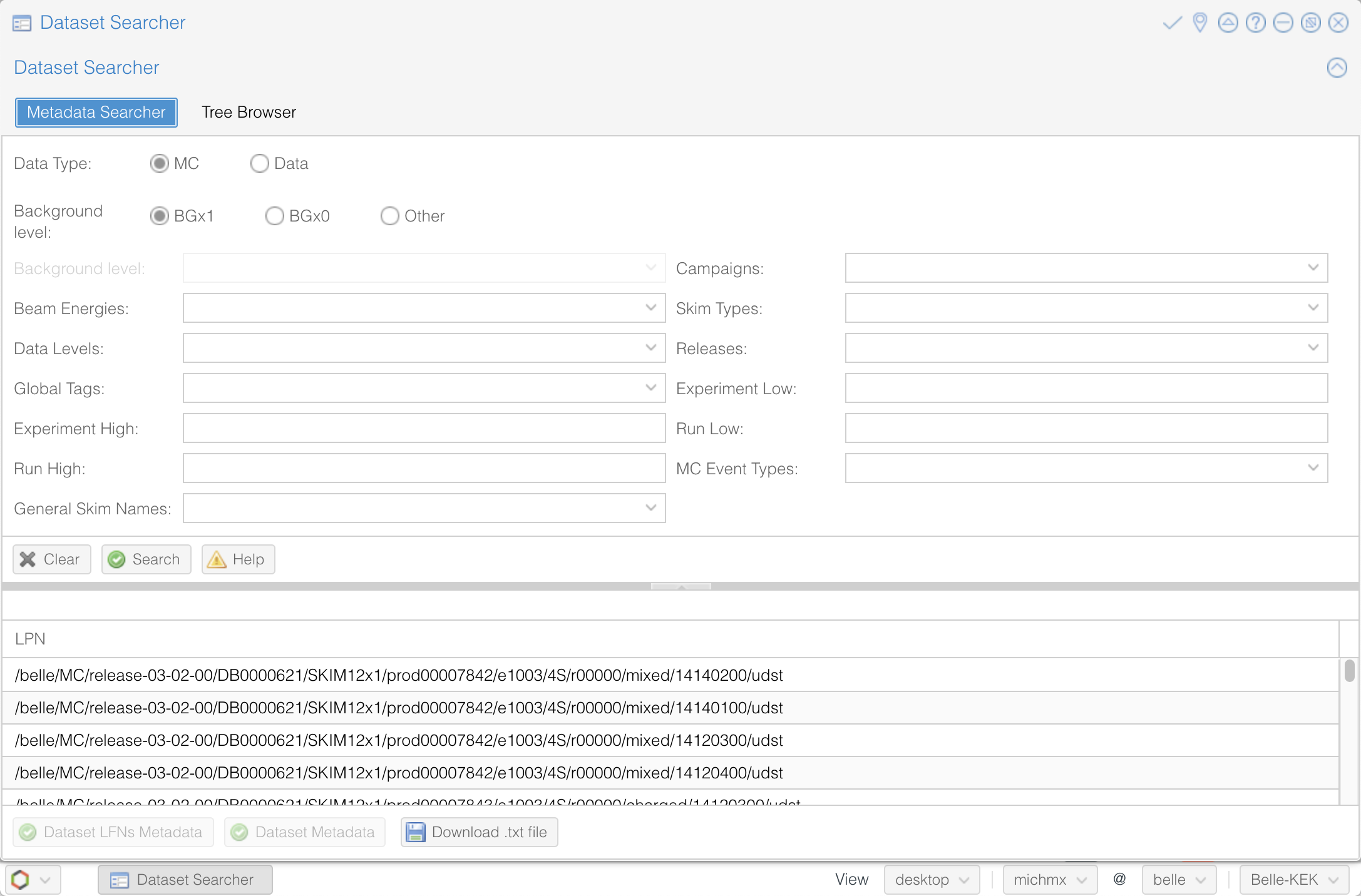
Fig. 21.35 The Dataset Searcher at the DIRAC web portal.¶
Note
Accessing the DIRAC web portal requires that your user certificate is installed in your web browser. See computing getting started for details.
The MC Event types box show by default the generic samples available (charged, mixed, uubar, etc.).
If you want to search
signal samples, you need to specify the signal event type.
Exercise
Open the Dataset Searcher and obtain the LFN of of the MC13a
signal sample B0 -> [J/psi -> e+e-][Ks -> pi+ pi-], with beam background (BGx1) in the simulation.
Hint
Search the signal event type of the decay.
Another hint
The event type is 1111540100.
Solution
/belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00012867/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/1111540100/mdst
Tip
You can download a list of LFNs from the Dataset Searcher using the button “Download txt file” at the bottom.
Another way to interact with the dataset searcher is using the command line tool gb2_ds_search.
Exercise
Set your gbasf2 environment and try to get the LFNs of MC uubar samples from MC13a, with beam energy of 4S
and background level BGx1 using gb2_ds_search.
Hint
Use --help and --usage to get all the available options
Solution
gb2_ds_search dataset --data_type mc --campaign MC13a --beam_energy 4S --mc_event uubar --bkg_level BGx1
Submit your first jobs to the Grid¶
As mentioned before, gbasf2 uses exactly the same steering files of basf2 to submit jobs to the grid. The basic usage is
gbasf2 <your_steering_file.py> -p <project_name> -s <available_basf2_release>
where project_name is a name assigned by you, and available_basf2_release is the available basf2 software
version to use.
Note
The maximum length for a project name is 32 characters.
Warning
Do not use special characters in the project names ($, #, %, /, etc.),
it could create problems with file names in some sites and in the databases
(we allow only [^a-zA-Z0-9+-_]).
Once located the dataset to use for your analysis, you can specify the LFN of the datablock to use as input with
with the flag -i.
Note
While the Dataset Searcher provides the LFN for datasets, gbasf2 uses for now datablocks as input. You need to append
sub00, sub01, ... to the LFNs provided by the Dataset Searcher (this will be fixed in the near future, sorry for
the inconvenience).
Everything clear? Ok, let’s submit your first jobs.
Warning
Remember: you must carefully check your jobs with a local computing system, e.g. KEKCC, before you submit jobs to GRID.
Let’s use the steering file located at
~michmx/public/tutorial2020/Reconstruct_Bd2JpsiKS_template.py on KEKCC (take a look at what contains).
If we are interested in running over a generic uubar sample, then the LFN of one datablock is
/belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00009436/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/uubar/mdst/sub00 (you obtained it in a
previous exercise, remember?).
With all this information, let’s submit the gbasf2 jobs:
gbasf2 -p gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs -s light-2002-ichep \
-i /belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00009436/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/uubar/mdst/sub00 \
~michmx/public/tutorial2020/Reconstruct_Bd2JpsiKS_template.py
A project summary and a confirmation prompt will be displayed after excecuting gbasf2
************************************************
*************** Project summary ****************
** Project name: gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
** Dataset path: /belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
** Steering file: /home/michmx/public/tutorial2020/Reconstruct_Bd2JpsiKS_template.py
** Job owner: michmx @ belle (105:58:39)
** Preferred site / SE: None / None
** Input files for first job: LFN:/belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00009436/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/uubar/mdst/sub00/mdst_000001_prod00009436_task10020000001.root
** Number of data sets: 1
** Number of input files: 803
** Number of jobs: 803
** Processed data (MB): 968305
** Processed events: 158623897 events
** Estimated CPU time per job: 3293 min
************************************************
Are you sure to submit the project?
Please enter Y or N:
After verifying that everything is correct, you can confirm the submission.
Question
What is the the basf2 release in the example above?
Solution
The basf2 light release is light-2002-ichep.
Tip
You can check which basf2 releases are available for running jobs on the grid using gb2_check_release.
Key points
A gbasf2 project can be submitted per datablock, NOT per dataset.
We will fix this in coming gbasf2 releases.
Inside the project, gbasf2 will produce file-by-file jobs.
The number of output files in the project will be the number of files in the input datablock.
Exercise
Submit a gbasf2 job with an steering file built by you in previous chapters of the book, for analyzing
a datablock of MC13a, MC Event Types charged with energy 4S and without beam background.
Use light-2008-kronos of basf2.
Remember:
Prepare your steering file.
Search the input datablock.
Submit using gbasf2.
Hint
Use the Dataset Searcher to locate MC13a datasets of MC Event Types charged and BGx0.
Additional hint
The input datablock may be obtained using
gb2_ds_search dataset --data_type mc --campaign MC13a --beam_energy 4S --mc_event charged --bkg_level BGx0
and adding sub00 at the end.
Solution
gbasf2 -i /belle/MC/release-04-00-03/DB00000757/MC13a/prod00009551/s00/e1003/4S/r00000/charged/mdst/sub00
-s light-2008-kronos -p myFirstProject <your steering file>
Submit jobs with multiple LFNs¶
If you want to submit a project with several datablocks, prepare a list of LFNs on a file and provide it to gbasf2 using
--input_dslist.
Tip
A quick way of appending sub00 to a list of LFNs obtained from the Dataset Searcher is using sed:
sed -i 's/mdst/mdst\/sub00/g' listOfLFNs.list
Monitoring jobs¶
There are two ways to monitor your jobs on the grid: command-line tools and the DIRAC web portal.
Monitoring in the terminal¶
In with command-line tools, you can use gb2_project_summary
to have an overview of your project (The flag -p will specify the project name):
gb2_project_summary -p gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
Project Owner Status Done Fail Run Wait Submission Time(UTC) Duration
=====================================================================================================
gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs michmx Running 0 0 5 0 2020-07-07 08:41:40 00:01:15
Tip
If no project name is specified, the tool will display information of your projects in the last month.
The gb2 tool gb2_job_status list all the jobs running in a project, including the status and minor status:
gb2_job_status -p gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
5 jobs are selected.
Job id Status MinorStatus ApplicationStatus Site
=============================================================================
161844659 Running Application Running LCG.KEK2.jp
161844660 Running Application Running LCG.KEK2.jp
161844661 Running Input Data Resolution Unknown LCG.Pisa.it
161844662 Running Application Running LCG.KEK2.jp
161844663 Running Application Running LCG.KEK2.jp
--- Summary of Selected Jobs ---
Completed:0 Deleted:0 Done:0 Failed:0 Killed:0 Running:5 Stalled:0 Waiting:0
Monitoring using the web portal¶
The second way is looking at the job monitor in the DIRAC web portal.
Open the portal, click on the logo at the bottom-left and go to Applications/Job Monitor.
You have to click on ‘Submit’ to display the information.
You should see something like this:
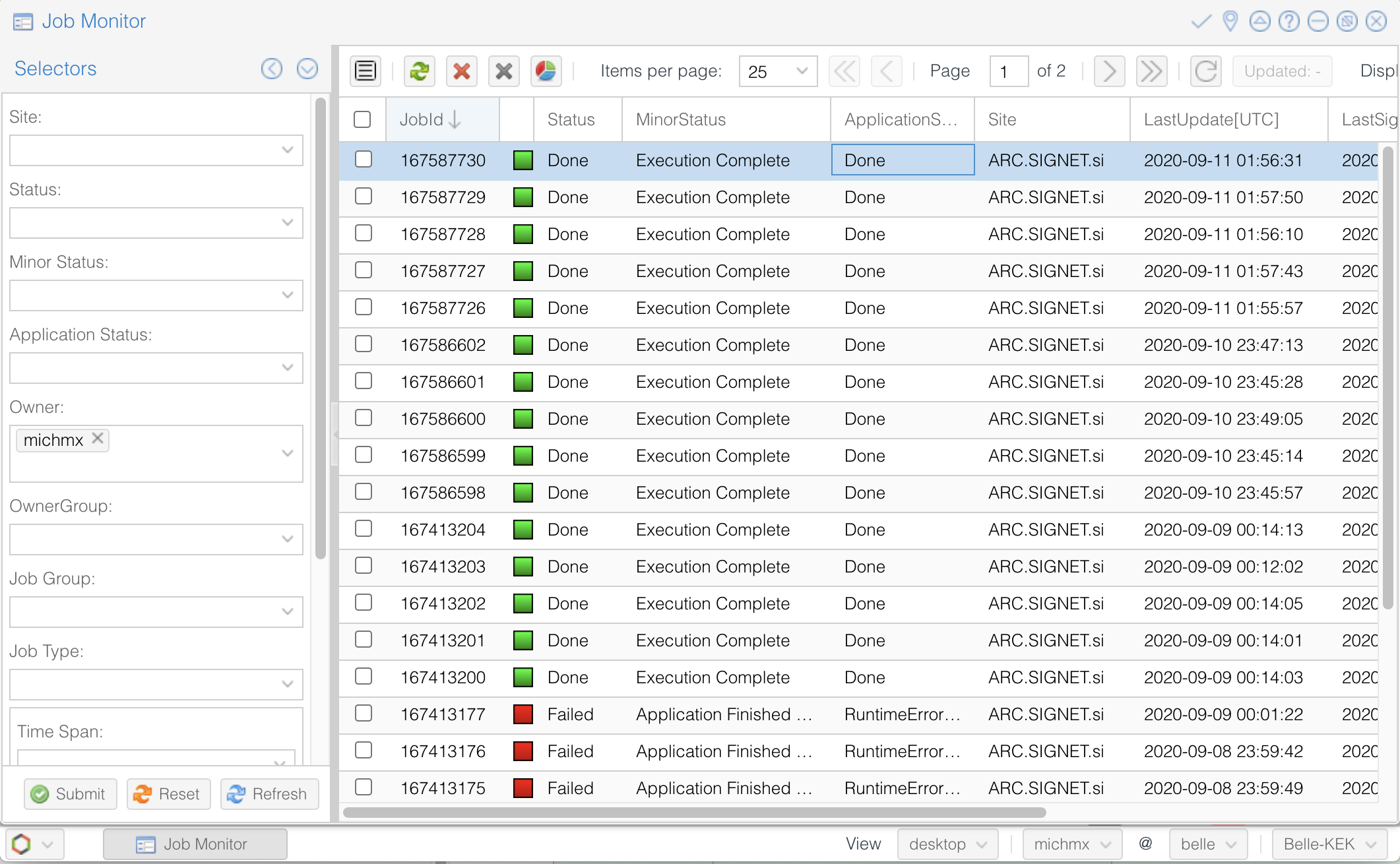
Fig. 21.36 The Job Monitor at the DIRAC web portal.¶
Tip
The Job Monitor includes many tools and features to track and manage your jobs, including a statistics panel (pie icon at the left-top). Get familiar with them.
Exercise
Monitor the jobs that you have submitted in the previous exercise. Wait until they finish successfully.
Hint
Do you see failed jobs? Go to the last section “Dealing with issues”.
Solution
Use the DIRAC web portal and open the Job Monitor. Jobs in green are in ‘Done’ status, while the failed ones are in red.
Downloading the output¶
If all your jobs finished successfully (have status ‘Done’), then you can download the output.
The output files will be located below your user space (/belle/user/<username>/<project_name>).
You can check the output using gb2_ds_list <project_name>:
gb2_ds_list gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_0.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_1.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_2.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_3.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_4.root
Tip
To see the size of your output and its location, you can use the flags -l and -lg.
To actually download the files, use gb2_ds_get:
gb2_ds_get gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
Download 5 files from SE
Trying to download srm://kek2-se03.cc.kek.jp:8444/srm/managerv2?SFN=/disk/belle/TMP/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_4.root to /home/michmx/gbasf2Tutorial/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_4.root
Trying to download srm://kek2-se03.cc.kek.jp:8444/srm/managerv2?SFN=/disk/belle/TMP/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_1.root to /home/michmx/gbasf2Tutorial/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_1.root
...
Successfully downloaded files:
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_4.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_1.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_3.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_0.root
/belle/user/michmx/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs/Bd2KpsiKs_2.root in /home/michmx/gbasf2Tutorial/gb2Tutorial_Bd2JpsiKs
Failed files:
Tip
Keep in mind: as far as you have a gbasf2 installation, you can submit jobs or download files from any machine.
Exercise
Download the output of your jobs submitted in a previous exercise. Verify that they are readable using ROOT.
Hint
First check that all your jobs finished successfully. Issues? Go to the next section.
Solution
Just use gb2_ds_get <your project name> (Easy, right?).
Dealing with issues¶
Sometimes, things do not go well. A few jobs can fail because a large list of reasons, like
A timeout in the transfer of a file between sites.
A central service not available for a short period of time.
An issue in the site hosting the job.
etc.
Some of my jobs failed¶
If you find that some of your jobs failed, most probably there was a temporal issue with your job or the site. You need to reschedule these jobs by yourself.
You can use gb2_job_reschedule -p <project name>:
gb2_job_reschedule --usage
Resubmit failed jobs or projects.
Only jobs which have fatal status (Failed, Killed, Stalled) are affected.
Exact same sandbox and parameters are reused. Thus you may need to submit different job if they are wrong.
By default, select only your jobs in current group.
Please switch group and user name by options.
All user's jobs are specified by '-u all'.
Examples:
% gb2_job_reschedule -j 723428,723429
% gb2_job_reschedule -p project1 -u user
Or you can use the job monitor in the DIRAC web portal, selecting the failed jobs and clicking the ‘Reschedule’ button.
All my jobs failed¶
If all your jobs failed, most probably something is wrong with the steering file or the gbasf2 arguments (Did you test your steering file locally before submitting the jobs?).
A useful way to track which was the problem is (if possible) downloading the output sandbox. It contains the logs related to your job.
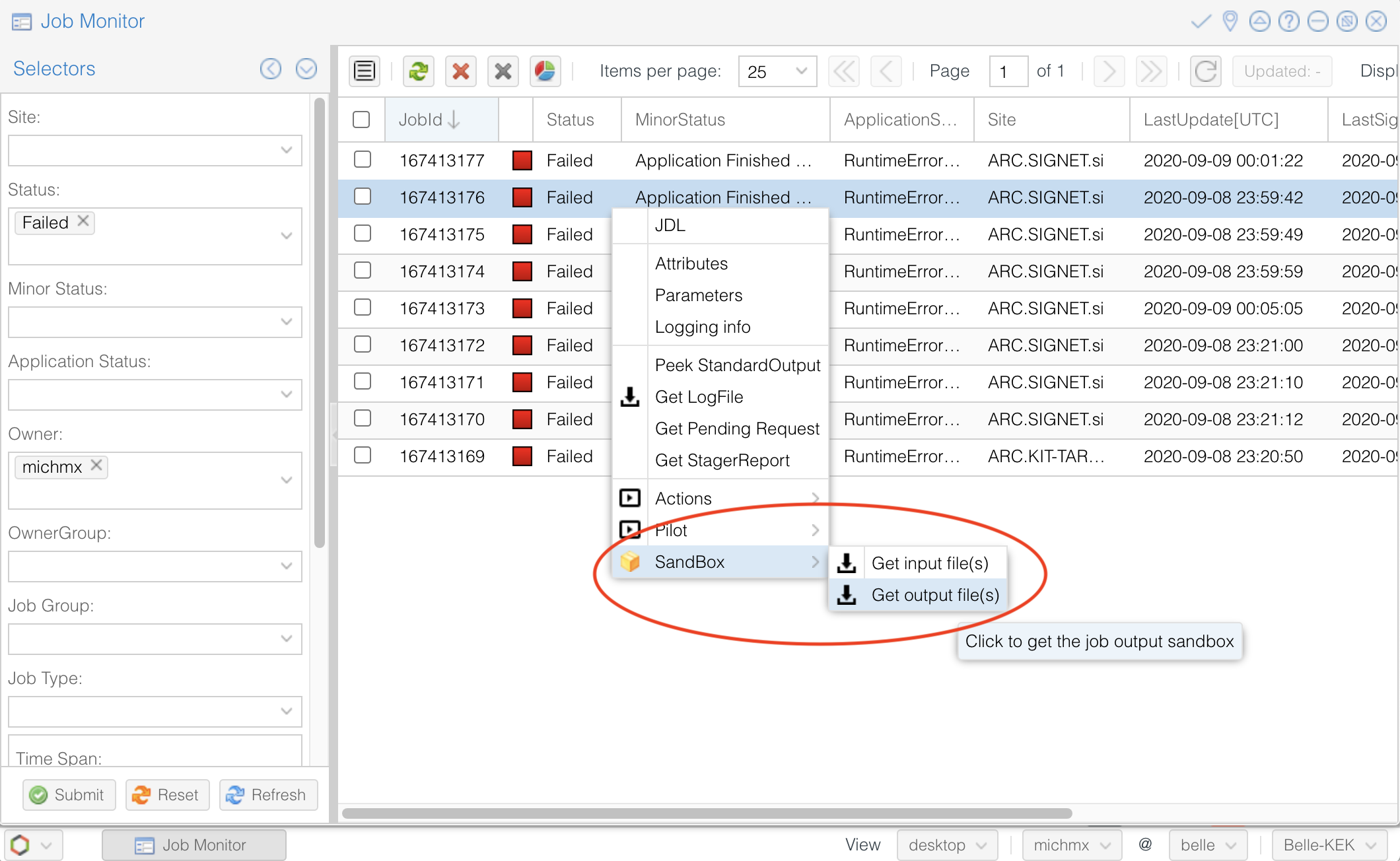
Fig. 21.37 How to download the output sandbox from the Job Monitor.¶
It is also possible to retrieve the log files directly from the command line using gb2_job_output:
gb2_job_output -j 161846653
download output sandbox below ./log/JOBID
1 jobs are selected.
Please wait...
Result for jobs: ['161846653']
=====================================================================================
Downloaded: "Job output sandbox retrieved in /home/michmx/gb2_tutorial/log/161846653"
Exercise
Download the output sandbox of one of your jobs. Check what is inside.
Hint
One of the logs inside may look very familiar.
Solution
The file basf2helper.py.log contains the actual output of your basf2 steering file executed on the grid site.
Where to go for help?¶
The comp users forum is the main channel of communication related to issues with the grid. Feel free to ask every time that you need help.
Additionally, some pages at Confluence are prepared with additional information:
Take a look to the gbasf2 tutorials (they contain some advanced topics not covered here).
You can also ask in questions.belle2.org.
Stuck? We can help!
If you get stuck or have any questions to the online book material, the #starterkit-workshop channel in our chat is full of nice people who will provide fast help.
Refer to Collaborative Tools. for other places to get help if you have specific or detailed questions about your own analysis.
Improving things!
If you know how to do it, we recommend you to report bugs and other requests
with JIRA. Make sure to use the
documentation-training component of the Belle II Software project.
If you just want to give very quick feedback, use the last box “Quick feedback”.
Please make sure to be as precise as possible to make it easier for us to fix things! So for example:
typos (where?)
missing bits of information (what?)
bugs (what did you do? what goes wrong?)
too hard exercises (which one?)
etc.
If you are familiar with git and want to create your first pull request for the software, take a look at How to contribute. We’d be happy to have you on the team!
Quick feedback!
Author of this lesson
Michel Villanueva